Amazon admits that it might have a problem with counterfeits. For the first time ever, the Seattle-based e-commerce giant made mention in its annual 10-K filing of the elephant on its platform: fakes. In a single line in the “risk factors” section of the yearly report it files with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, the Jeff Bezos-owned company stated, “We may be unable to prevent sellers in our stores or through other stores from selling unlawful, counterfeit, pirated, or stolen goods, selling goods in an unlawful or unethical manner, violating the proprietary rights of others, or otherwise violating our policies.”
The arguably long-overdue admission comes amidst mounting criticism of and a growing number of lawsuits filed against the world’s largest e-commerce platform, most of which have accused Amazon of being “complicit” in the widespread sale of counterfeit goods on its site. These qualms have largely followed from Amazon’s 2014 move to enable China-based entities to sell directly to Amazon shoppers in the West, and in the process, growing its sales by a whopping 20 percent in a single year and enabling its total revenues to blaze past the $100 billion mark for the first time.
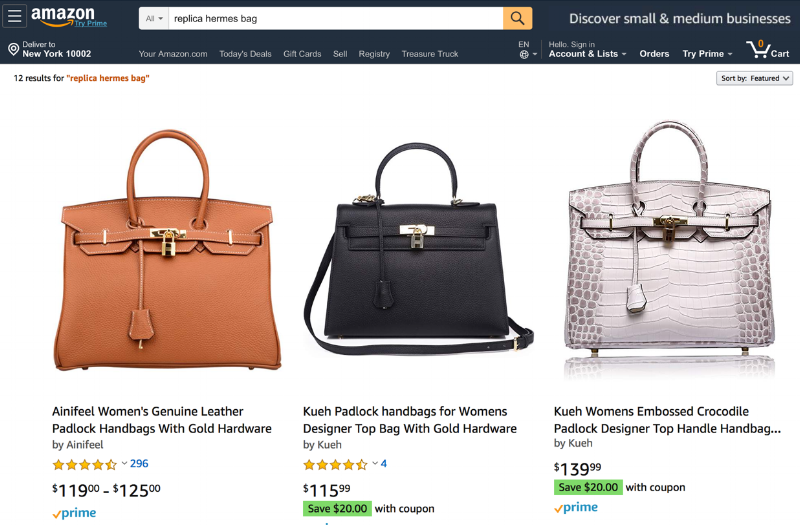
To date, Amazon-specific criticism has come from a multitude of sources, including this website, which questioned the merit of its “zero tolerance” policy when it comes to fakes in light of the fact that searches for things, such as “Fake Gucci” bags and “replica Birkin” bags, readily return results for counterfeit goods.
Independent sellers — forced to directly compete on Amazon’s marketplace with scammers who blatantly steal their intellectual property — have spoken out. Casey Hopkins, the founder of industrial design firm Elevation Lab, penned a highly-cited post on his website last year, calling out Amazon for directly profiting from the sale of fakes.
Brands also have not been shy about taking the $1 billion giant to task. Birkenstock, for instance, publicly cut off Amazon, not once, but twice, “terminating [its] business relations with Amazon” in the U.S. and the European Union, due to Amazon’s alleged failure to commit to “proactively policing its site for counterfeits.”
Still yet, at least one trade group, the American Apparel & Footwear Association, has urged the U.S. Trade Representative to include Amazon’s international arms to its annual blacklist of “Notorious Markets,” asserting that its “members are growing increasingly frustrated with how [Amazon] protects their intellectual property.”
These complaints, among others, have coincided with legal action. Mercedes Benz’s parent company, Daimler AG, filed suit against Amazon in November 2017 on trademark infringement grounds, claiming that in additional to its problematic marketplace, Amazon’s model for labeling products as “Shipped from and sold by Amazon.com” amounts to a “fraudulent business act.” In particular, Daimler asserted that by using the “Shipped from and sold by Amazon.com” model, “Amazon itself sells infringing items” and “capitalizes upon and profits from Daimler [and other brands’] reputation and goodwill.”
Less than a year after that legal battle was initiated, fashion brand Ella Moss filed a trademark infringement suit against Amazon, alleging that the giant launched a similarly-named private label, Ella Moon, with a similar aesthetic and lookalike designs in an effort to confuse consumers and steal sales from Ella Moss.
All the while, Amazon’s PR team has been adamant that it “strictly prohibits the sale of counterfeit products and invest heavily – both funds and company energy – to ensure our policy against the sale of such products is followed.”
According to CNBC, the newly-added acknowledgement of counterfeit goods in its 10-K filing “reflects Amazon’s increased concern over the counterfeit problem on its marketplace, as the words ‘counterfeit’ and ‘pirated’ were never mentioned in its annual filing before.”